Technology in Outer Space
The role of technology in outer space exploration is multifaceted and plays a critical role in enabling humanity to understand, access, and operate in the challenging and remote environment of space. From spacecraft design and propulsion to life support systems and scientific instrumentation, technology is at the heart of every aspect of space exploration.
1. Spacecraft Design and Development
Technology is essential for the design, development, and construction of spacecraft used in space exploration. Advances in materials science, engineering, and computer-aided design have revolutionized spacecraft construction. These advancements have led to the creation of increasingly capable and durable spacecraft, including satellites, space probes, rovers, and crewed vehicles. Through technological innovation, spacecraft have become more efficient, reliable, and capable of enduring the rigors of space travel.
2. Propulsion Systems
Technological advancements in propulsion systems have been fundamental to expanding the reach of space exploration. Traditional chemical rockets, while still in use, have been complemented by advanced propulsion concepts such as ion drives, solar sails, and nuclear propulsion. These technologies have enabled spacecraft to travel further, faster, and more efficiently, opening up new frontiers for exploration within our solar system and beyond.
3. Communication and Data Transmission
Effective communication and data transmission are essential for maintaining contact with spacecraft and retrieving scientific data.
1. Communication Systems: Advanced communication systems are essential for transmitting data between spacecraft, satellites, and ground stations. These systems use technologies like radio waves, antennas, and transmitters to send and receive signals over vast distances. They also employ modulation techniques to encode data onto the carrier signal and error correction codes to ensure accurate transmission.
2. Deep Space Network (DSN): The DSN is a network of ground-based antennas strategically located around the world to communicate with spacecraft in deep space. These antennas use advanced technologies to track and communicate with spacecraft, ensuring continuous contact and data transmission. They employ high-gain antennas, signal amplifiers, and sophisticated signal processing techniques to maintain reliable communication over long distances.
3. Data Compression and Storage: Due to the limited bandwidth available for data transmission in space, efficient data compression techniques are employed to reduce the size of the transmitted data. Advanced algorithms and technologies are used to compress and decompress data without significant loss of information. Additionally, onboard storage systems are used to temporarily store data before transmission, allowing for efficient data transfer during specific communication windows.
4. Optical Communication: Optical communication, also known as laser communication, is an emerging technology for high-speed data transmission in space. It uses laser beams to transmit data, offering higher bandwidth and data rates compared to traditional radio frequency communication. Optical communication systems require advanced laser technology, precise pointing mechanisms, and sensitive detectors to establish
4. Scientific Instrumentation
Technology has played a crucial role in the development of scientific instruments used in outer space. These instruments are designed to analyze the composition of celestial bodies, measure radiation, capture high-resolution images, and conduct a wide range of experiments in the space environment. From spectrometers and cameras to seismometers and particle detectors, these instruments provide valuable data that enhances our understanding of the cosmos.
1. Space Telescopes: Space telescopes, like the Hubble Space Telescope and the James Webb Space Telescope, utilize advanced optics, detectors, and imaging technologies to observe distant galaxies, stars, and planets. They are designed to operate in the harsh conditions of space and provide high-resolution images and spectroscopic data.
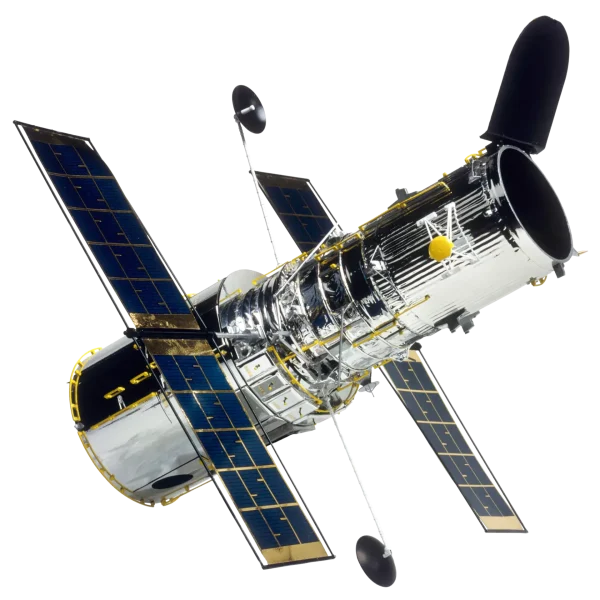

2. Spectrometers: Spectrometers used in space missions are designed to analyze the composition and properties of celestial objects. They employ technologies like diffraction gratings, detectors, and onboard data processing to measure the spectrum of light emitted or absorbed by distant objects.
3. Particle Detectors: Particle detectors are used in space missions to study cosmic rays, high-energy particles, and radiation. They employ technologies like solid-state detectors, scintillators, and charge-coupled devices (CCDs) to measure the energy, charge, and trajectory of particles.
4. Remote Sensing Instruments: Remote sensing instruments, such as radar and lidar systems, are used to study the Earth’s atmosphere, surface, and climate from space. These instruments use advanced technologies like laser beams, microwave signals, and high-resolution imaging to gather data about the planet’s features and changes over time.
5. Space Probes and Rovers: Space probes and rovers, like the Mars rovers (e.g., Curiosity and Perseverance), are equipped
5. Life Support and Habitability
For crewed missions, technology is critical for providing life support systems to sustain human life in space. These systems include air revitalization, water recycling, waste management, and radiation protection. Advanced life support technologies ensure the health and well-being of astronauts during long-duration missions and are essential for enabling sustained human presence in space.
6. Robotics and Automation
Robotic systems and autonomous technologies have expanded the capabilities of space exploration. Robotic probes and rovers have been instrumental in exploring the surfaces of planets, moons, and asteroids, providing valuable scientific data and imagery. Advances in robotics and automation have enabled the assembly of large structures in space, such as the International Space Station, and have the potential to revolutionize future space construction and resource utilization efforts.
7. Earth Observation and Environmental Monitoring
Space-based technologies provide valuable data for monitoring Earth’s environment, including climate patterns, natural disasters, and changes in ecosystems. Satellites equipped with remote sensing instruments play a critical role in environmental monitoring, disaster response, and the study of Earth’s interconnected systems.
8. Navigation and Positioning
Precise navigation and positioning technologies are essential for spacecraft to accurately travel to their intended destinations and conduct scientific missions. Global navigation satellite systems, such as GPS and Galileo, provide crucial positioning information for spacecraft in Earth orbit and beyond.
9. Materials and Structures
Advancements in materials science and engineering have led to the development of lightweight, durable materials and innovative structural designs.
1. Lightweight Metals: Aluminum and titanium alloys are commonly used in spacecraft construction due to their lightweight nature and high strength-to-weight ratio. These materials help reduce the overall weight of the spacecraft, making it easier to launch and maneuver in space.
2. Composite Materials: Carbon fiber-reinforced polymers (CFRP) and other composite materials are used in space technology for their high strength, low weight, and resistance to extreme temperatures. These materials are often used in the construction of rocket fairings, satellite components, and structural elements.
3. Heat-resistant Materials: Spacecraft experience extreme temperature variations in space, ranging from extreme cold to intense heat during re-entry. Thermal protection systems (TPS) are used to protect the spacecraft from these temperature extremes. Materials like ceramic tiles, ablative materials, and carbon-based composites are used in TPS to provide heat resistance.
4. Radiation Shielding: Spacecraft and space stations need to protect astronauts from harmful radiation in space. Materials like polyethylene, water, and aluminum are used as radiation shielding to absorb or deflect radiation particles.
5. Inflatable Structures: Inflatable structures, also known as expandable habitats, are being developed for use in space stations. These structures are made of flexible materials that can be compacted for launch.






