AI in Diagnostics: Faster, More Accurate Diagnoses
AI has made significant strides in diagnostics, where its ability to process large datasets and recognize patterns is invaluable. In this article, we look at how AI is transforming healthcare in general and its future applications. In fields such as radiology, dermatology, and pathology, AI-powered tools can analyze medical images to detect anomalies that may be too subtle for human eyes. These tools can assist physicians in identifying cancers, cardiovascular diseases, and neurological disorders more accurately and at earlier stages.
For example, AI algorithms have been shown to outperform radiologists in detecting early-stage breast cancer in mammograms by reducing false positives and negatives. AI systems like Google’s DeepMind and IBM’s Watson Health are already being used in medical settings to assist doctors in diagnosing complex conditions faster and more efficiently.
Advantages:
- Increased accuracy: AI can analyze large amounts of data and find patterns that may not be immediately obvious, leading to more accurate diagnoses.
- Early detection: AI-powered tools can help identify diseases like cancer in their earliest stages, when treatment is more effective.
- Time efficiency: AI can significantly reduce the time it takes to make a diagnosis, allowing doctors to focus on patient care.

Disadvantages:
- Reliance on data quality: AI’s performance is highly dependent on the quality and quantity of data. Poor data can lead to inaccurate diagnoses.
- Lack of human intuition: AI lacks the human intuition and experience that can be critical in making nuanced medical decisions.
AI in Personalized Treatment: Tailoring Therapies for Individual Patients
AI is also being used to create personalized treatment plans that take into account an individual patient’s unique genetic makeup, lifestyle, and environmental factors. This approach, known as precision medicine, can lead to more effective and targeted treatments. For example, AI algorithms can analyze genetic data to predict how a patient will respond to different medications, allowing doctors to select the most appropriate treatment with fewer trial-and-error attempts.
Moreover, AI can optimize treatment plans for chronic conditions like diabetes or hypertension by continuously analyzing patient data from wearable devices or mobile health apps. These AI-driven systems can recommend adjustments to medication dosages, exercise routines, and diet based on real-time data, making healthcare more responsive and personalized.
Advantages:
- Precision medicine: AI enables highly personalized treatment plans that can improve patient outcomes.
- Real-time adjustments: AI can monitor patients continuously and suggest adjustments to their treatment plans based on data.
- Reduced trial and error: Personalized treatments reduce the need for trial-and-error approaches, making treatment more efficient and less stressful for patients.
Disadvantages:
- High costs: Developing and implementing AI-based personalized treatment systems can be expensive.
- Data privacy concerns: Using AI for personalized treatment requires access to sensitive patient data, raising concerns about data security and privacy.
AI in Drug Discovery: Accelerating the Path to New Treatments
Drug discovery is a lengthy and expensive process, often taking years to bring a new drug to market. AI has the potential to significantly speed up this process by analyzing chemical compounds, predicting drug interactions, and identifying potential candidates for further research. AI algorithms can process vast amounts of data from clinical trials, patient records, and scientific literature to identify promising drug candidates faster than traditional methods.
For instance, AI company Insilico Medicine has used machine learning to identify novel molecules for potential drugs. In 2020, they discovered a new drug candidate for fibrosis in just 46 days—a process that traditionally takes several years.
Advantages:
- Faster drug discovery: AI can drastically reduce the time required to identify and develop new drugs, bringing life-saving treatments to market more quickly.
- Cost reduction: AI helps reduce the costs associated with drug development by streamlining research and clinical trials.
- Improved success rates: AI can identify potential drug candidates with a higher likelihood of success in clinical trials.
Disadvantages:
- Regulatory challenges: The use of AI in drug discovery presents regulatory challenges, as current frameworks are not fully equipped to evaluate AI-generated drugs.
- Potential job displacement: AI-driven drug discovery could lead to the displacement of traditional researchers and laboratory workers, raising concerns about job security.
AI in Robotic Surgery: Enhancing Precision and Minimizing Risks
Robotic-assisted surgery has become increasingly common in hospitals, with AI playing a crucial role in enhancing precision and reducing human error. AI-powered surgical robots, such as the da Vinci Surgical System, can assist surgeons by providing enhanced dexterity, precision, and control. These systems can perform delicate procedures with greater accuracy than human surgeons, minimizing risks such as tissue damage and blood loss.
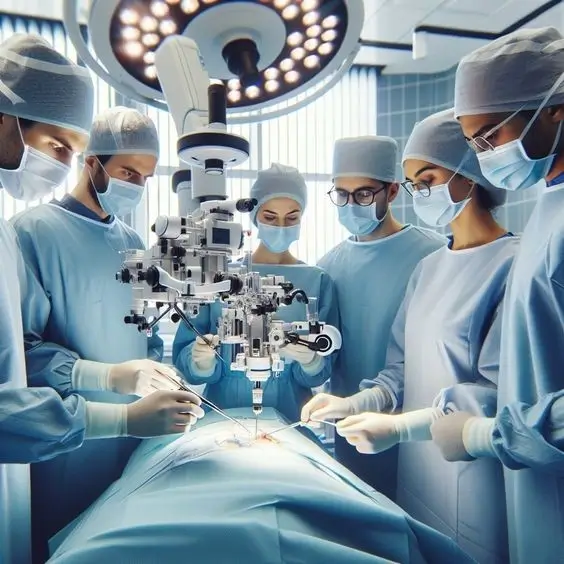
Additionally, AI algorithms can analyze surgical data in real-time, offering insights and recommendations to surgeons during operations. This can improve surgical outcomes, reduce recovery times, and lower the risk of post-operative complications.
Advantages:
- Increased precision: AI-powered robotic surgery systems can perform complex and delicate procedures with high accuracy.
- Reduced risk of complications: AI helps minimize human error, leading to fewer surgical complications and faster recovery times.
- Access to remote areas: AI-powered tele-surgery allows skilled surgeons to perform operations remotely, giving patients in underserved areas access to expert care.
Disadvantages:
- High costs: Robotic surgery systems and AI-driven tools are expensive to implement and maintain, limiting their availability in some healthcare settings.
- Potential for over-reliance: While AI can enhance surgical outcomes, over-reliance on these systems may reduce the surgeon’s hands-on skills and decision-making abilities.
AI in Telemedicine: Expanding Access to Healthcare
AI-powered telemedicine platforms have gained widespread popularity, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic. These platforms use AI to analyze patient data, conduct virtual consultations, and even diagnose conditions remotely. AI chatbots and virtual assistants can interact with patients to collect symptoms, provide medical advice, and recommend next steps. In some cases, AI systems can even prescribe medications based on the information provided by the patient.
By expanding access to healthcare, especially in rural and underserved areas, AI-powered telemedicine can help bridge the gap between patients and healthcare providers. AI can also help manage the workload of healthcare professionals by handling routine tasks such as appointment scheduling, symptom assessment, and follow-up care.
Advantages:
- Increased access to care: AI-powered telemedicine allows patients in remote or underserved areas to access healthcare services without having to travel.
- Convenience: Patients can receive medical advice and treatment from the comfort of their homes, reducing the need for in-person visits.
- Efficiency: AI can automate administrative tasks, such as appointment scheduling and patient triage, freeing up time for healthcare providers to focus on patient care.
Disadvantages:
- Quality of care concerns: While AI-powered telemedicine can be convenient, it may not always provide the same quality of care as in-person visits, particularly for complex medical conditions.
- Digital divide: Patients without access to reliable internet or smart devices may be excluded from the benefits of AI-powered telemedicine, exacerbating healthcare disparities.
Ethical and Legal Challenges of AI in Healthcare
As AI becomes more prevalent in healthcare, ethical and legal concerns are emerging. One of the most significant challenges is ensuring that AI systems are fair, transparent, and unbiased. AI algorithms can inadvertently perpetuate biases present in the data they are trained on, leading to disparities in healthcare outcomes. For example, an AI system trained on data primarily from one demographic may be less effective at diagnosing conditions in other demographics, contributing to healthcare inequality.
Additionally, the use of AI in healthcare raises questions about accountability. If an AI system makes a wrong diagnosis or recommends an ineffective treatment, who is responsible—the AI developer, the healthcare provider, or the hospital? Establishing clear guidelines for accountability is crucial as AI continues to play a more significant role in medical decision-making.
Privacy concerns are also a major issue, as AI systems require access to vast amounts of sensitive patient data. Ensuring that patient data is protected and used ethically is essential to maintaining trust in AI-driven healthcare systems.
The Future of AI in Healthcare
The future of AI in healthcare looks promising, with continuous advancements in machine learning, data analysis, and robotics paving the way for even more innovative solutions. In the coming years, we can expect to see AI playing an even more significant role in areas such as genomics, predictive analytics, and population health management.
- AI in genomics: AI can analyze genetic data to identify disease-causing mutations and predict an individual’s risk of developing certain conditions, enabling earlier interventions.
- Predictive analytics: AI can analyze historical data to predict future health outcomes, helping healthcare providers make more informed decisions and prevent diseases before they occur.
- Population health management: AI can analyze large datasets to identify trends and patterns in population health, enabling healthcare systems to allocate resources more effectively and improve public health outcomes.
While AI holds immense potential for revolutionizing healthcare, its integration must be approached with caution. Ensuring that AI systems are transparent, unbiased, and secure will be critical to their success in improving patient care.
Conclusion: The Balancing Act of AI in Healthcare
AI is undeniably transforming healthcare, from faster diagnoses to personalized treatment and beyond. The advantages of AI, such as increased accuracy, efficiency, and access to care, are profound. However, there are also significant challenges to address, including data privacy concerns, ethical considerations, and the potential for job displacement.
As AI continues to evolve, the healthcare industry must strike a balance between leveraging its benefits and mitigating its risks. By doing so, we can ensure that AI remains a valuable tool in delivering high-quality, equitable healthcare to all.

For further reading and resources on how AI is transforming healthcare:
- World Health Organization – Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: WHO – AI in Healthcare
- Harvard Business Review – How AI is Changing Healthcare: HBR – AI in Healthcare






