Businesses everywhere are discovering that their most powerful advantage no longer sits in a physical server room, but in the cloud. Cloud computing has emerged as one of the most significant technological shifts of the 21st century, enabling companies of all sizes to access powerful computing resources through the internet. From data storage and software applications to analytics and customer management systems, the cloud has become the backbone of modern business operations.
What makes cloud computing truly transformative is its ability to offer flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency. Businesses can now scale their resources up or down based on demand, reduce expenses associated with on-premises servers, and collaborate seamlessly across global teams.
This technology has changed how businesses operate, deliver services, and engage with customers. By moving critical operations to the cloud, enterprises are unlocking new opportunities for efficiency, flexibility, and growth, opening the door to a more connected and intelligent future.
In this article, we will explore cloud computing, the services it offers, different deployment models, the benefits of cloud computing, and how organizations are using it.
Understanding Cloud Computing and How It Works
Cloud computing enables businesses to access technology resources, such as servers and databases, without owning them physically. Instead, these resources are rented online, making it easier and more cost‑effective to leverage advanced tools without heavy infrastructure investments.
According to Danielle (2025), Cloud computing refers to using the internet to access computing services, such as servers, storage, databases, software, and data analysis tools, instead of buying and maintaining physical equipment in your business premises. It allows businesses to rent technology resources whenever they need them. This model replaces the traditional approach of maintaining costly in-house infrastructure with a more flexible, scalable, and cost-effective solution.
At its core, cloud computing is built on the idea of sharing computing power, software, and data storage over the internet. Instead of businesses owning their own servers, companies and individuals pay to access a shared pool of virtual resources, such as processing power, storage, and networking, hosted in remote data centers managed by cloud providers.
Cloud computing connects users to a platform through the internet, where they can “rent” the computing services they need. A central system manages the communication between user devices and the cloud’s servers, ensuring smooth data exchange. Additionally, cloud computing has built-in security and privacy features that help protect sensitive information throughout the process, ensuring that business-sensitive data cannot be accessed without authorization.
The cloud computing system is not the same for all businesses, as each has different needs and strengths. Cloud computing offers flexibility, allowing you to customize solutions to your business’s needs. This adaptability enables enterprises to respond more quickly to market shifts and operate with greater flexibility.
Cloud Computing Service Models
Cloud computing service models describe the different layers of services that cloud providers offer to your business; hence, this determines how much control and responsibility you maintain over their systems. By understanding these options, your business can choose the approach that best supports your needs, simplifies operations, and accelerates innovation in the cloud. The following are the models as per Justine (2025)
a. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides the basic building blocks of cloud computing, enabling users to access virtualized computing resources over the internet. With this, your business does not need to manage physical hardware for servers, storage, or networking, as it can easily access them through the infrastructure-as-a-service model of cloud computing. For instance, Amazon Web Services, a cloud computing and web hosting company in Kenya, provides businesses with flexible online infrastructure services, including servers, storage, and databases.
b. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS offers a complete development environment where developers can build, deploy, and manage applications without managing the underlying infrastructure. Businesses that develop Softwares mainly use this cloud computing service. With platform-as-a-service, they can focus on coding while the platform handles servers, operating systems, and databases.
c. Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS delivers fully managed software applications over the Internet, usually via subscription. Users can access the software through a web browser, eliminating the need for local installations. Popular SaaS applications include Google Workspace, Salesforce, Slack, Zoom, and Dropbox.
Read Also: Leveraging Artificial Intelligence for Small Business Success
Cloud Computing Deployment Models
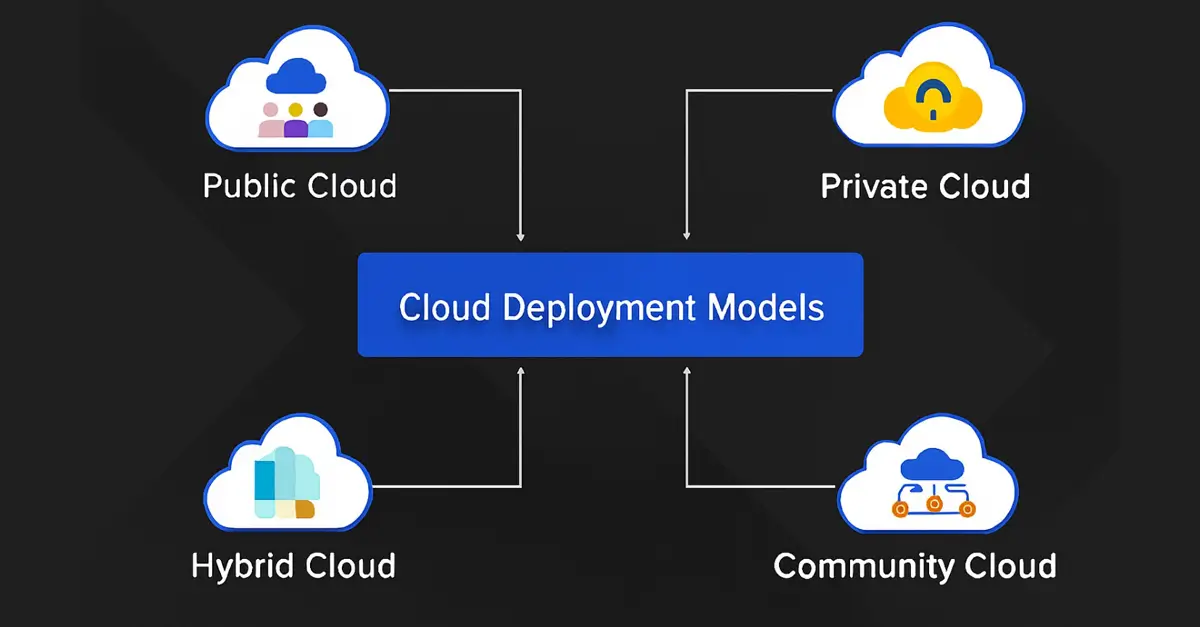
Cloud computing deployment models are how cloud services are set up, hosted, and managed. This determines the level of access and control organizations have over the computing resources. Understanding these options is essential because each model comes with unique advantages and trade-offs. By choosing the model that best aligns with their needs, businesses can optimize their operations and support future growth. A study done by Lucy (2025) highlights the following cloud computing models.
a) Public Cloud
This is a cloud environment accessible to anyone over the internet. In this model, computing resources such as storage, applications, and processing power are shared among many users, which makes it one of the most common and affordable cloud deployment options.
All resources in a public cloud are hosted in the provider’s own data centers. Businesses simply connect to these services as needed, without having to manage any physical hardware. Public cloud platforms can handle large numbers of requests and offer almost unlimited resources, making them ideal for organizations that need to scale quickly and cost-effectively.
b) Private Cloud
This type of cloud environment is dedicated to a single organization. Unlike the public cloud, where hardware and resources are shared with others, the private cloud is reserved exclusively for one user or company. This setup offers greater control, security, and customization, making it ideal for businesses with strict data protection and regulatory requirements.
The key difference between public and private clouds lies in how the underlying hardware is managed. In a private cloud, the infrastructure can be hosted on-site within the company or in a secure, dedicated space managed by a cloud provider. Because it is used by only one organization, the private cloud is sometimes called an “internal cloud,” allowing teams to access systems and services securely from within the company or across multiple locations.
c) Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud combines public and private cloud environments, enabling a company to use its on-premises systems while leveraging public cloud services. These two environments are connected and function as a single system, making this model especially useful for organizations seeking a gradual, flexible transition to the cloud.
Many businesses choose a hybrid cloud because security and compliance requirements prevent them from moving all their data to the public cloud. With this model, sensitive information can remain in private, on-premises systems, while less sensitive workloads and applications run in the public cloud. This approach ensures strong security and control, while also delivering the scalability and cost benefits of public cloud services.
d) Community Cloud
A community cloud is a shared cloud environment designed for several organizations that have similar needs, standards, or regulatory requirements. Instead of each organization building its own private cloud, they use a common platform where resources, services, and infrastructure are shared among members of the same community. The participating organizations, a third-party provider, or both can manage this model.
The key benefit of a community cloud is that it supports organizations with shared goals, such as healthcare providers, financial institutions, and government agencies, by enabling them to collaborate securely while meeting industry-specific compliance standards. It offers a balance of shared costs and specialized control, making it a practical option for groups with similar business or regulatory requirements.
Some Examples of Cloud Computing?

Cloud computing offers a wide range of services that cater to nearly every business need. From productivity tools and communication platforms to advanced development services and storage solutions, cloud computing enables users to work, collaborate, and innovate from virtually anywhere. A study by Kinza (2025) highlights the following examples of cloud computing in our daily lives.
a. Google Docs and Microsoft 365
Cloud-based productivity suites like Google Docs and Microsoft 365 allow employees in your business to create, edit, and store documents, spreadsheets, and presentations online. Because these tools are accessible online from any device, users can work remotely, collaborate in real time, and access their files anytime, anywhere.
b. Email, Calendar, Skype, and WhatsApp
Services such as email platforms, online calendars, Skype, and WhatsApp rely on the cloud to store and manage data remotely. This enables users to access messages, appointments, and communications from any device, ensuring seamless connectivity and organization regardless of location.
c. Zoom and Microsoft Teams
Communication and collaboration platforms like Zoom and Microsoft Teams are cloud-based, providing video and audio conferencing, file sharing, and real-time collaboration. Meetings can be recorded and stored in the cloud, allowing participants to access content later, which supports flexibility and productivity across teams.
d. Amazon Web Services (AWS)
AWS is a serverless compute service that allows you to run code without managing servers. It will enable the developers to run application code without managing servers. This pay-as-you-go model adapts automatically to changing workloads and usage, making it efficient for applications with variable demand. Other major cloud providers, such as Google Cloud and Microsoft Azure, offer similar serverless computing options through Cloud Run Functions and Azure Functions.
e. Salesforce
Salesforce is a cloud-based customer relationship management (CRM) platform that helps businesses manage sales, marketing, and customer service operations. By storing and analyzing data in the cloud, Salesforce enables companies to gain insights, track customer interactions, and improve decision-making.
f. Dropbox
Dropbox is a cloud storage service that allows users to store files online and access them from any device. It also supports file sharing and collaboration, making it easy for teams to work together on documents and projects without relying on local storage or email attachments.
Read Also: Data-Driven Decision-Making for Businesses
Benefits of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has transformed the way businesses operate, offering a wide range of advantages that improve efficiency, flexibility, and competitiveness. By leveraging cloud services, organizations can reduce costs, enhance collaboration, scale resources dynamically, and focus more on innovation rather than infrastructure management. A study by Bandana (2025) highlights the following benefits.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Cloud computing allows your business to pay only for the resources it actually uses, eliminating the need for costly investments in physical hardware and data centers. This model reduces both capital and operational expenses while freeing IT teams to focus on strategic initiatives.
- Scalability – Cloud services can be quickly scaled up or down based on demand. This flexibility ensures that businesses have the right amount of computing power, storage, and network capacity at any time, without overprovisioning or wasting resources.
- Collaboration and Accessibility– Cloud platforms enable real-time collaboration by allowing multiple users to access and work on duplicate files and applications simultaneously. Teams can work from anywhere, on any device, enhancing productivity and streamlining workflows.
- Reliability and Redundancy – Most cloud providers maintain robust, redundant infrastructure to minimize downtime and prevent data loss. Built-in backup and disaster recovery capabilities ensure businesses maintain continuity even in the face of unexpected disruptions.
- Innovation and Time-to-Market – Cloud computing provides ready-to-use tools, services, and APIs that accelerate development and deployment. Organizations can launch new products and services faster, reduce development costs, and stay competitive in rapidly changing markets.
How Are Organizations Using Cloud Computing in Today’s World?

Cloud computing has become a cornerstone of modern business operations, enabling organizations to operate more efficiently, innovate faster, and respond quickly to changing market conditions. Companies across industries leverage the cloud for infrastructure, data management, application development, and analytics. Here are some of the key ways organizations are using cloud computing today, as per Avani (2025)
i. Infrastructure Scaling
Cloud computing enables businesses to scale their infrastructure up or down based on demand. For example, your business can quickly increase computing capacity during peak shopping seasons to manage higher traffic and scale it back during quieter periods, reducing costs and maintaining performance.
ii. Disaster Recovery
Organizations can use cloud services for secure backup and disaster recovery, eliminating the need to build and maintain additional physical data centers. Digital assets are stored and replicated in the cloud, ensuring business continuity and enabling rapid recovery in case of unexpected disruptions.
iii. Data Storage
Cloud storage provides a cost-effective, scalable solution for managing large volumes of data. It offers accessibility, redundancy, and simplified data sharing across distributed teams. Cloud platforms also make backup, recovery, and data analysis easier, helping businesses optimize their storage while maintaining security and compliance.
iv. Application Development
Cloud platforms provide pre-configured development environments, frameworks, and services that accelerate application development and deployment. Developers can focus on creating features and functionality. At the same time, the cloud handles infrastructure setup and management, reducing time-to-market for new applications.
v. Big Data Analytics
The cloud’s vast computing resources make it ideal for processing and analyzing large datasets. Cloud-based analytics platforms help organizations extract insights, perform complex calculations, and support data-driven decision-making. The scalability of the cloud ensures that even large workloads are handled efficiently, providing faster access to actionable insights.
Read Also: The Role of Technology in Boosting Business Efficiency
Conclusion
Cloud computing has transformed how organizations access, manage, and utilize IT resources. By offering key advantages such as cost-effectiveness, scalability, and global reach, the cloud enables businesses to focus on their core operations while cloud providers handle infrastructure management. You can use cloud computing across a variety of your daily business operations, such as data storage, data recovery, infrastructure scaling, and application development. With this variety of service and deployment models, cloud computing gives organizations the flexibility to design their cloud environments to meet specific needs. As a platform for innovation, efficiency, and collaboration, cloud computing has become an essential tool for organizations aiming to stay competitive and thrive in today’s digital world.






